
薛佳 女士
数据中心高级经理,北京汇捷通国际展览有限公司
| 电话 | +86 21 63232733 |
|---|---|
| 传真 | +86 21 63232733 |
| 邮箱 | katelyn.xue@interfoam.cn |
| 地址 | 上海市黄浦区广东路500号世界贸易大厦5层 |

在挤出发泡中,在使用物理发泡剂的条件下制造高质量发泡产品会存在两个混合问题。一是如何使发泡剂在聚合物熔体中能实现饱和的密集混合,二是熔体/发泡剂溶液的均化问题。发泡产品的泡孔质量(即泡孔尺寸完整性和尺寸分布)与后者密切相关,即熔体温度分布,尤其是对于厚板产品。溶体温度相差几度,泡孔膨胀和泡孔强度就可能会出现很大的变化。在高产量的条件下,厚度方向上的温度变化是一个难以控制的参数。
In foam extrusion, there are two mixing concerns in making a high-quality foam product while using physical blowing agent. One is the intensive mixing for blowing agent to saturate in the polymeric melt. Two is the homogenizing the melt/blowing agent solution. Foam cell quality (i.e., cell size integrity and size distribution) is strongly related to the latter, namely, melt temperature distribution, especially for thick board products. A few degrees difference, the cell expansion and cell wall strength may show a big variation. At high throughput, the melt temperature difference across the thickness is a limiting parameter.
众所周知,在挤出发泡中,同样存在熔体流动的温度变化很难控制的问题。聚合物本身是一种较差的热导体。在设计中,产生破碎以允许在厚度方向上进行混合的操作是非常具有挑战性的。对于分散混合,利用高剪切区是一种常见的做法。但是其伴随而来的剪切生热不仅会增加电机的扭矩,还会加大以稳定熔体发泡为目的的冷却设备的负载。而一个有效的解决方案是在流道上设置一个屏障螺纹,以达到强制缠绕和展开熔体的目的,使熔体可以分成一个长条从而连续接触冷却筒,如图1所示。尽管熔体泵送能力在一定程度上受到了影响,但总体上来说,利大于弊。
It has been well known that in foam extrusion the temperature variation across the melt flow is hard to control. Polymer itself is a poor thermal conductor. Generating disruption to allow mixing in the thickness direction is very challenging in design. For dispersive mixing, high shear zone is a common practice. The concomitant shear heat generation causes not only increased torque to the motor, but also more load in taking heat away to stabilize the melt foaming. One clever solution is to set up a barrier screw across the channel to force winding and unwinding that the melt bulk can be divided into a long strip to contact the cooling barrel continuously as shown in Fig. 1. Although melt pumping capability is somewhat compromised, overall it is more positive than negative.
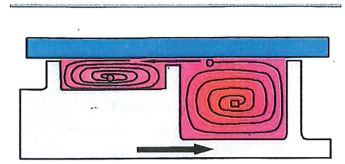
图1: 流过屏障螺棱的流动方式
It can be imagined that the entry point and exit may exhibit enough temperature variation to cause foaming uniformity concerns. An improved version is illustrated in Fig. 2.The holed shell with cooling oil through it demonstrated benefits in foam quality and throughput. Since it has two pairs of 90 degree turns and stagnant areas, left over may be hanging on the corners, which can cause extra time in purging for color change. More efforts were made on hole size and cooling path optimization in the last decade. Lately, hole geometry has being investigated to further improve the melt temperature distribution in the thickness distribution with less stagnant areas.
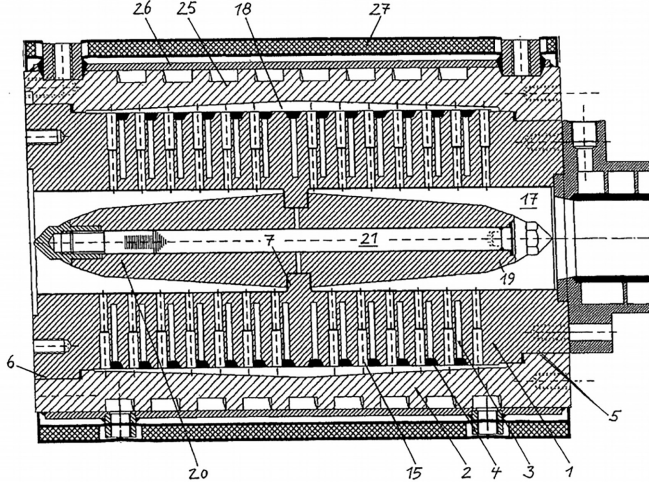
图2: 熔体冷却器DE专利号: 202005001985
Fig. 2: Melt Cooler DE patent: 202005001985
翻译自北京化工大学-何亚东老师团队
为了更好的体验
请竖屏浏览